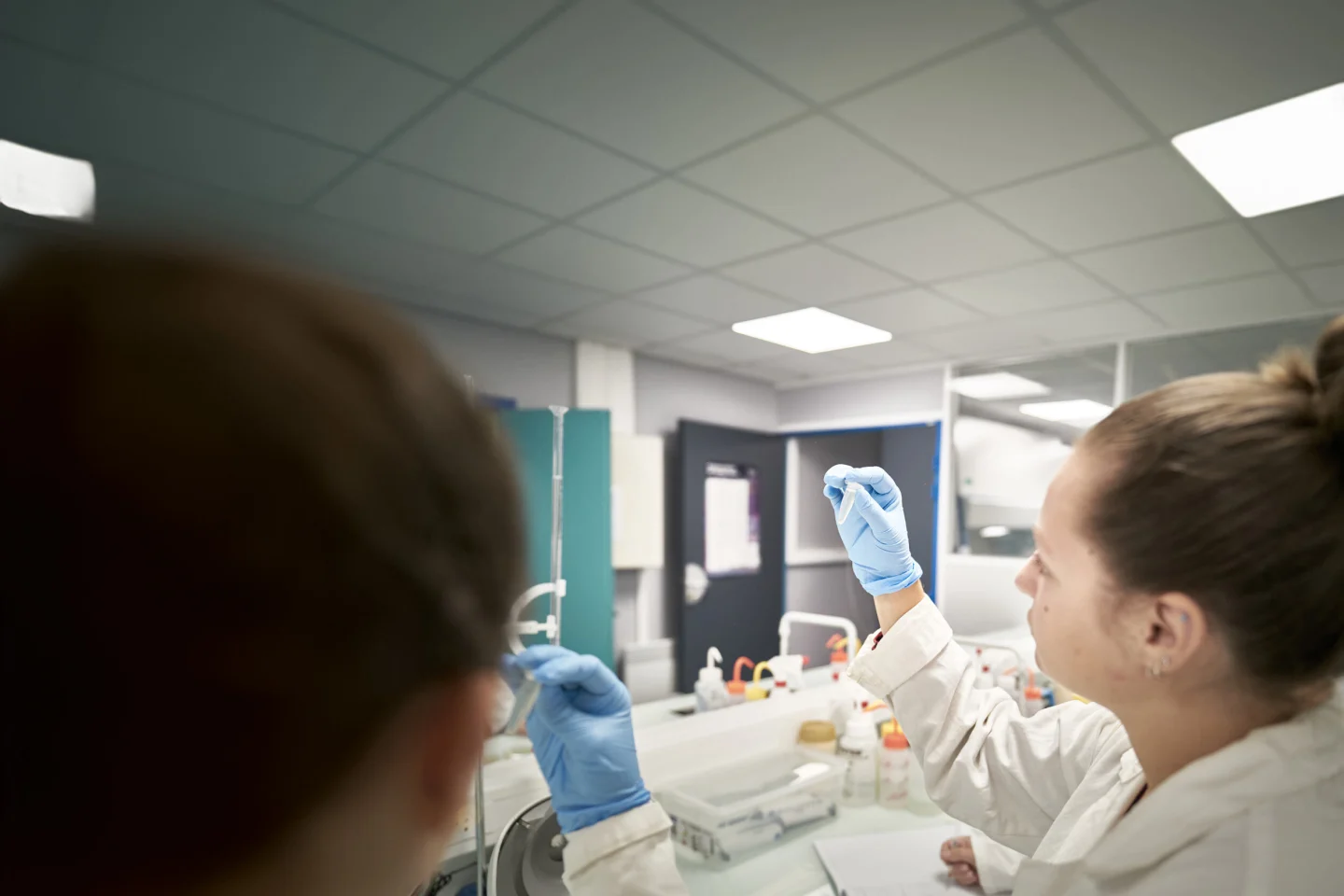

Engineering Degree in Biotechnology
SupBiotech delivers a Degree of Engineering in Biotechnology.
It is also possible to study at SupBiotech for one semester or one year and being awarded a school certificate. It allows you to discover SupBiotech’s teaching methods and experience French lifestyle.
Foundation years
The Preparatory Cycle privileges independence and the learning of fundamentals, either in Paris or in Lyon. Students may choose to complete the first two years of this cycle entirely in English with foreign students in the Anglophone section.

1st year : Discovery
Establish a base in the training of engineers competent in their field and open to the outside world.
2nd year : Development
Determine the approach to the professional world and further extend one’s scientific knowledge.
The engineering programme
The engineering programme lasts three years enabling any future trainee engineers to achieve the required cultural dimension for an engineer in Biotechnology from the SupBiotech Institute.

3rd year : Develop further
Open up to an international level and become the main actor of your training thanks to a personalized curriculum

4th year : Decide
Determine preferred professional choices in Majors and Minors.

5th year : Integration
Professionalize your educational path with lessons in English. Finalize the personalization of your curriculum.